Blog
Can Eating Certain Foods Really Cause Inflammation and Pain?
Many people are shocked when they hear this question answered honestly:
Yes—certain foods can absolutely drive inflammation and pain in the body.
Not just temporarily.
Not just in the gut.
But systemically—affecting joints, muscles, fascia, nerves, energy levels, and even how well your body heals.
At Camarata Chiropractic & Wellness, we see this every day. Patients come in with chronic pain, stiffness, fatigue, headaches, or slow recovery and say:
“I eat pretty healthy… why do I still hurt?”
The missing piece is often food-driven inflammation.
Inflammation: The Root of Most Chronic Pain
Inflammation is not inherently bad. Acute inflammation is a normal healing response.
The problem is chronic, low-grade inflammation—the kind that quietly lingers and keeps tissues irritated, sensitized, and slow to heal.
When inflammation becomes persistent:
-
Pain receptors become hypersensitive
-
Muscles stay tight
-
Joints stiffen
-
Fascia loses elasticity
-
Recovery slows
-
Fatigue increases
Food is one of the most powerful drivers of this inflammatory state.
How Food Triggers Inflammation in the Body
Certain foods can trigger inflammation through several mechanisms:
1. Blood Sugar and Insulin Spikes
Foods high in refined carbohydrates and sugar cause rapid blood sugar spikes, followed by crashes. Over time, this leads to insulin resistance and increased inflammatory signaling.
2. Immune System Activation
Some foods provoke an immune response—even without classic allergy symptoms. This immune activation releases inflammatory chemicals that can affect the entire body.
3. Gut Barrier Breakdown
Inflammatory foods can damage the intestinal lining, leading to increased intestinal permeability (leaky gut). Once the gut barrier is compromised, inflammatory compounds enter the bloodstream and circulate systemically.
4. Nervous System Sensitization
Chronic inflammation heightens nervous system sensitivity, making pain feel stronger and more persistent—even without structural damage.
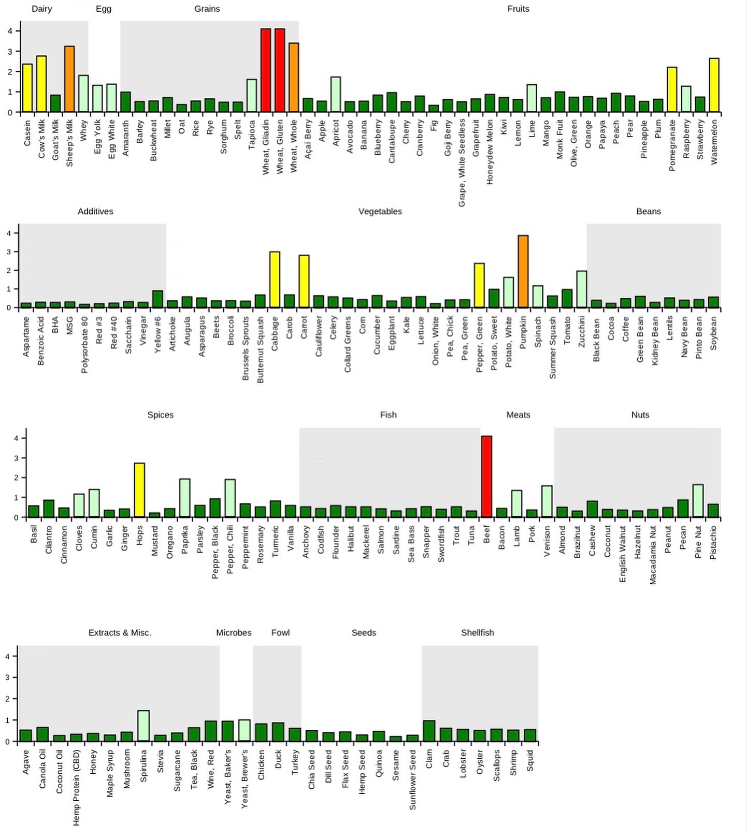
Common Inflammatory Foods That Drive Pain
While everyone responds differently, some foods are common culprits when it comes to inflammation and pain.
Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates
Excess sugar fuels systemic inflammation, increases oxidative stress, and disrupts energy regulation. It also worsens joint pain, muscle soreness, and recovery.
Gluten-Containing Grains
For some individuals, gluten triggers immune activation, gut inflammation, and joint or nerve pain—even without celiac disease.
Processed Seed Oils
Oils high in omega-6 fatty acids (such as corn, soybean, and canola oil) can promote an inflammatory imbalance when consumed in excess.
Dairy
Certain forms of dairy may trigger inflammation through immune reactions, hormone responses, or digestive stress.
Ultra-Processed Foods
Additives, preservatives, emulsifiers, and artificial sweeteners can disrupt gut bacteria and promote chronic inflammation.
Why Inflammatory Foods Cause Pain Outside the Gut
One of the biggest misconceptions is that food-related inflammation should only cause digestive symptoms.
In reality, inflammation from food often shows up as:
-
Neck, back, or joint pain
-
Muscle tightness
-
Headaches or migraines
-
Plantar fasciitis
-
Hip or shoulder stiffness
-
Fatigue and brain fog
-
Slow injury recovery
Pain is often the late-stage signal of an internal inflammatory process that’s been building for years.
Why Your Labs Can Look “Normal” but You Still Hurt
Many patients are told:
“Your blood work looks fine.”
That doesn’t mean inflammation isn’t present.
Food-driven inflammation often exists at a functional level, not a disease level. Standard labs frequently miss:
-
Early immune activation
-
Gut barrier dysfunction
-
Food sensitivities
-
Tissue-level inflammation
This is why people can feel inflamed long before anything shows up on routine testing.
Food Sensitivities vs. Food Allergies
Food allergies cause immediate reactions.
Food sensitivities cause delayed, cumulative inflammation.
Symptoms may appear:
-
Hours later
-
The next day
-
Or after repeated exposure
This makes identifying problem foods nearly impossible without proper testing or structured elimination strategies.
How Inflammatory Foods Affect Healing and Recovery
When inflammatory foods remain in the diet:
-
Tissue regeneration slows
-
Chiropractic adjustments don’t hold as long
-
Soft tissue therapies feel temporary
-
Fascia stays restricted
-
Pain keeps returning
Healing requires an internal environment that supports repair—not one constantly triggering immune stress.
A Whole-Body Approach to Reducing Food-Driven Inflammation
At Camarata Chiropractic & Wellness, we don’t separate nutrition from pain care.
Our comprehensive approach may include:
-
Chiropractic care to regulate the nervous system
-
SoftWave Tissue Regeneration Therapy to stimulate healing
-
Red light therapy to support cellular and mitochondrial health
-
Fascia-focused therapies to restore tissue glide
-
Food inflammation and gut health guidance
-
Lifestyle strategies to reduce total inflammatory load
When food-driven inflammation is addressed, patients often experience faster recovery, less pain, and more consistent progress.
Final Thought
So—can eating certain foods really cause inflammation and pain?
Absolutely.
Food can either:
-
Calm the nervous system and support healing
or -
Quietly fuel inflammation and keep pain alive
If you’re doing everything else right but still struggling, the missing piece may not be another treatment—it may be what’s on your plate.
Healing happens when the body is no longer fighting itself.
Get a Hold of Us
If you’re ready to address inflammation and pain at the root—not just manage symptoms—we’re here to help.
Camarata Chiropractic & Wellness
3237 Union St, North Chili, NY 14514
Phone: 585-617-4145
Email: info@camaratachiropractic.com
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/camaratachiropractic
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/camarata_chiro/
Schedule your consultation today and take the next step toward long-term healing and resilience.
New Patient Scheduler Online Here!

The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Content shared on this website is not meant to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any condition. Individual health needs and circumstances vary. Always consult with your healthcare provider or speak with our team at Camarata Chiropractic & Wellness before making changes to your health, nutrition, hydration, exercise, or lifestyle routines.
‹ Back